19 June 2015, Carbon Brief, The Atlantic ‘conveyor belt’ and climate: 10 years of the RAPID project: A global project that’s been instrumental in shaping scientists’ understanding of how the oceans affect our climate celebrated its tenth birthday recently. A new paper published in Science looks back at 10 years of the RAPID project, which has been keeping tabs on how heat moves around in the Atlantic Ocean since 2004. Over its short lifetime, the project has thrown up a few surprises. Parts of the Atlantic circulation seem to have slowed down, though whether that’s down to human activity remains to be seen. Carbon Brief talks to one of RAPID’s founding scientists, Prof Harry Bryden from the National Oceanography Centre in Southampton, about the project. Read More here
Global heat transport
Above about 1,000 metres in the North Atlantic, warm water flows northwards from the equator towards the poles, releasing heat as it goes. The water cools and sinks at high latitudes, returning southwards towards the equator at much deeper depths.
This is known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and forms part of aglobal ocean conveyor belt that transports heat all around the world.
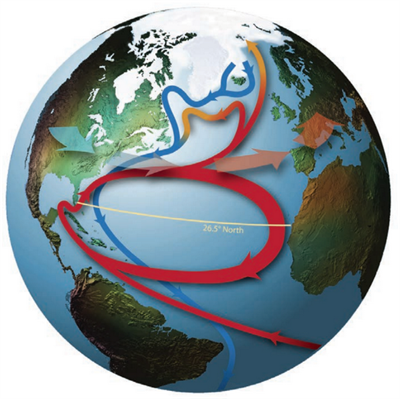
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). Warm water flows north in the upper ocean (red arrows) then sinks and returns south as deep cold water (blue arrows) Source: Srokosz & Bryden ( 2015) Supplementary material
